Some learning notes from https://github.com/donnemartin/system-design-primer
Basic Concepts
Trade-offs
Scalablity vs Performance
Good Scalablity: if we increase the resource in the system, the performance increase proportion to the resources added.
An always-on service is said to be scalable if adding resources to facilitate redundancy does not result in a loss of performance
from : A Word on Scalability
- performance problem -> system slow for a single user
- scalablity problem -> fast for a single user but slow under heavy load.
Why difficult:
- Cannot be after-thought
- Heterogeneity: some nodes are able to process fatster or store more data than other nodes, but they all rely on uniformity either break down under these conditions or underutilize the newer resources..
- different generations of hardware
- resources become more cost-effective
How to consider:
- consider along which axis we expect the system to grow
- where redundancy is required
- how one should handle heterogeneity in the system
- architects are aware of which tools they can use for under which conditions
Latency & throughput
Latency: the time to perform some action or to produce some result.
Throughput: the number of such actions or results per unit of time.
Generally aim for maximum throughput with acceptable latency.
Availablity & Consistency
Recap: the CAP theorem
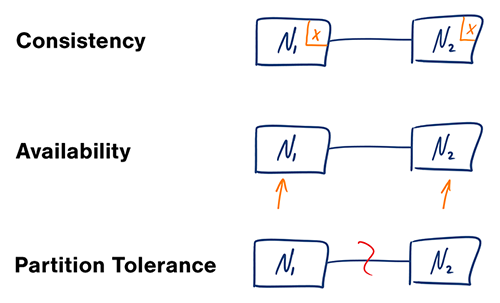
image from: CAP theorem revisited
In a distributed computer system, you can only support two of following gauarantees:
- Consistency: Every read receives the most recent write or an error.
- Availability: Every request receives a response, without gauarantee that it contains the most recent version of write.
- Partition Tolerance: The system continues to operate despite arbitary partitioning dur to network failures.
Networks are not reliable, so a system always need to support partition tolerance.
We need trade-off between availability and consistency.
CP - Consistency and partition tolerance
-
Waiting for a response from the partitioned node might result in a timeout error.
-
good if the system reuqires atomic reads and writes
AP - Availability and partition tolerance
- Responses return the most readily available version of the data available on any node, which might not be latest.
- Writes might takes some time to propagate when partition is resolved.
- good if system allows for eventual consistency or the system needs to continue working despite external errors.
Consistency patterns
Weak consistency
After a write, reads may or may not see it. A best effort approach is taken.
- seen in systems such as memcached.
- works well in real time use cases such as video chat, VoIP and multiplayer games.
Eventual Consistency
After a write, reads will eventually see it (within milliseconds). Data replicated asynchronously.
- seen in system such as DNS and email.
- works well in highly available system.
Strong Consistency
After a write, reads will see it. Data is replicated synchronously.
- seen in file system and RDBMSes.
- works well in systems that need transactions.
Domain Name System (DNS)
Translate domain name into ip address
DNS is hierarchical with a few authoritative servers at the top level.
- NS record (name server) - specifies the DNS servers for your domain/subdomain
- MX record (mail exchange) - specifies the mail servers for accepting messages
- A record (address) - points a name to an IP address
- CNAME (canonical) - point a name to another name or CNAME (examples.com to www.examples.com) or to a A record.
Some DNS services can route traffic through various methods:
- Weighted round robin
- Prevent traffic from going to servers under maintenance
- Balance between varying cluster sizes
- A/B testing
- Latency-based
- Geolocation-based
Disadvantages: DNS
- Accessing a DNS servers introduces a slight delay, although mitigated by caching
- DNS server management could be complex, generally managed by gov, ISPs, and large companies.
- DNS services recently come under DDoS attack.
Load Balancing algorithm
-
Round Robin
-
balancing in a cyclic fashion
- not able to treat servers differently
- good for clusters with idential stats
-
-
Weighted Round Robin
-
Still cyclical
-
higher spec gain higher proportion
-
tell weight beforehand
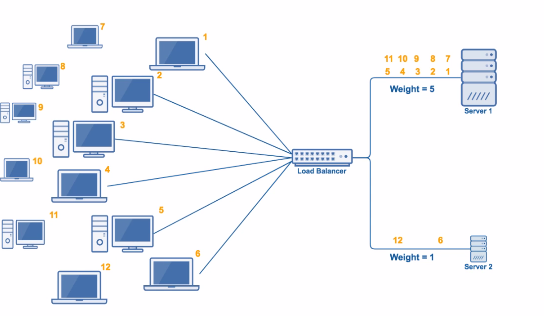
-
may have multiple criterions for weight
-
-
Least Connections
- Connections may last long
- determine with server has least connections and make routing to that server
-
Weighted Least Connection
- weight for capacities beforehand
- consider weight \& Leaset number
-
Random
- rand generator
- distribute evenly
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
CDN is a globally distributed networks of proxy servers, serving content from locations closer to the user.
Generally static files such as HTML/CSS/JS, photos and videos are served from CDN, although some CDNs such as Amazon’s CloudFront support dynamic content. The site’s DNS resolution will tell clients which server to contact.
Servering content from CDN improve performance:
- users receive content from data centers close to them
- You services do not have to serve requests that the CDN fulfills
Push CDNs
Push CDNs receives new content whenever changes occur on your server.
Content is uploaded only when it is new or changed, minimize traffic bu maximizing storage.
- Sties with a small amount of traffic or sites with content that isn’t often updated work well with push CDNs
- Content is placed on the CDNs once
- you take full responsibility for prociding content, uploading directly to the CDN and rewriting URLs to point to the CDN.
Pull CDNs
Pull CDNs grab new content from your server when the first user requests the contetnt.
You leave the content on you server and rewrite URLs to point to the CDN. This result in a slower request until the content is cached on the CDN.
-
TTL determins how long content is cached.
- Minimize storage space on CDN but create redundant traffic
- Sites with heavy traffic work well wiht pull CDNs, as traffic is spread out more evenly with only recently-requested content remaining on the CDN.
Disadvantages
- CDN costs could be significant depending on traffic, though this should be weighed with additional costs you would incur not using a CDN.
- Content might be stale if it is updated before the TTL expires it.
- CDN requre changing URLs for static content to point to the CDN.
Load Balancer
Load balancer distribute incoming client requests to computing resources such as application servers and databases.
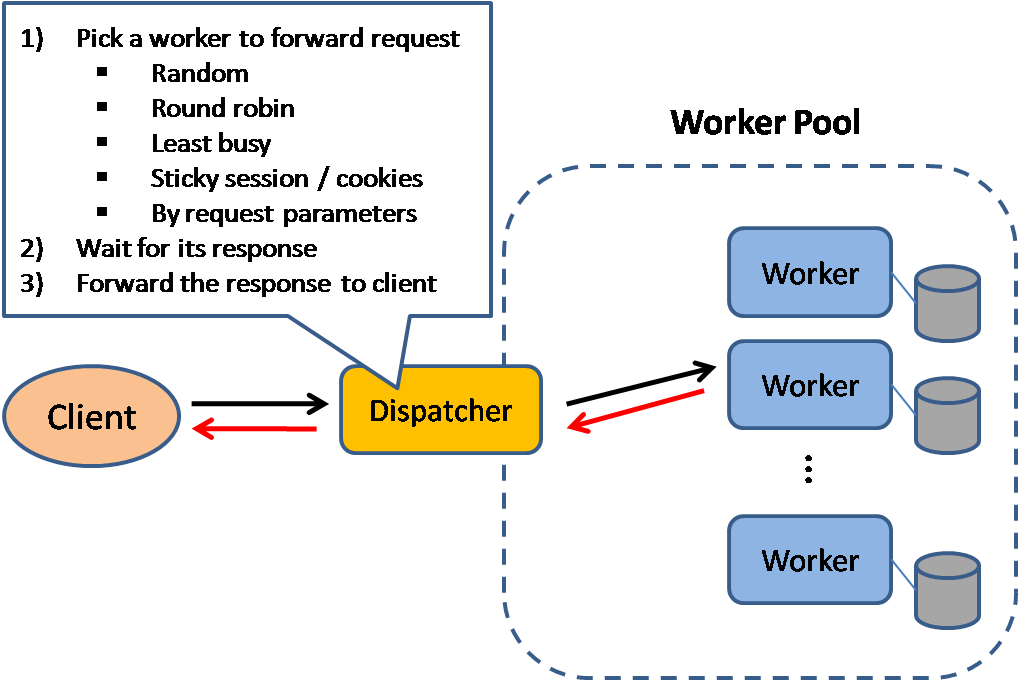
Effective at:
- Preventing requests from going to unhealthy servers
- Preventing overloading resources
- Helping elimintae a single point of failure
Additonal benefits:
- SSL termination - Decrypt incoming requests and encrypt server responses so backend servers do not have to perform these potentially expensive operations
- Session persistence - Issue cookies and route a specific client’s requests to same instance if the web apps do not keep track of sessions
Common to set multiple load balancers, either in active-passive or active-active mode.
- active-passive
- only active server handles traffic
- heartbeat sent between active and passive server on standby.
- If heartbeat interrupted, passive server takes over active’s IP and resumes service.
- active-active
- Both servers managing traffic
- If public facing, the DNS need to know about the public IPs of both servers
- If internal facing, application logic would need to konw about both servers
- also refer to as master-master failover
Route traffic based on various metrics:
- random
- least loaded
- Session/Cookies
- Round Robin or weighted round robin
- Layer 4
- Look at info at transport layer to decide how to distribute requests
- Generally involves source, destination IP address, and port in the header, but not the contents of the packet.
- Forward network packets to and from the upstream server, performing Network Address Translation (NAT).
- Layer 7
- Look at application layer to decide how to distribute requests.
- involve content of the header, message and cookies
- L7 balancers terminate network traffic, reads the message, makes a load balancing decision, then opens a connection to the selected server.
- E.g. L7 load balancer can direct video traffic to servers that host videos while directing more sensitive user billing traffic to security-hardened servers.
Horizontal scaling
Improve performance and scalability. Scaling out using commodity machines is more cost efficient and results in higher availability than scaling up single server on more expensive hardware, called Vertical scaling.
Disadvantages: horizontal scaling
- introduce complexity and involves cloning servers
- Servers should be stateless: they should not contain any user-related data like sessions or profile pictures
- Sessions can be stored in a centralized data store such as a database (SQL, NoSQL) or persistent cache (Redis, Memcached).
- Downstream servers such as caches and databases need to handle more simultaneous connections as upstream servers scale out.
Disadvantage: Load balancer
- The load balancer can become a performance bottleneck if it does not have enough resources or if it is not configured propoerly.
- Introducing a load balancer to help eliminate a single point of failure results in increased complexity.
- A single load balancer is a single point of failure, configuring multiple load balancers further increases complexity.
Reading : Inside NGINX: How we designed for performance \& Scale
How NGINX handles multiple connections within a single process
Common way to design network applications is to assign a thread or process to each connection, this architecture is simple and easy to implement, bt it does not scale when the application needs to handle thousands of simultaneous connections.
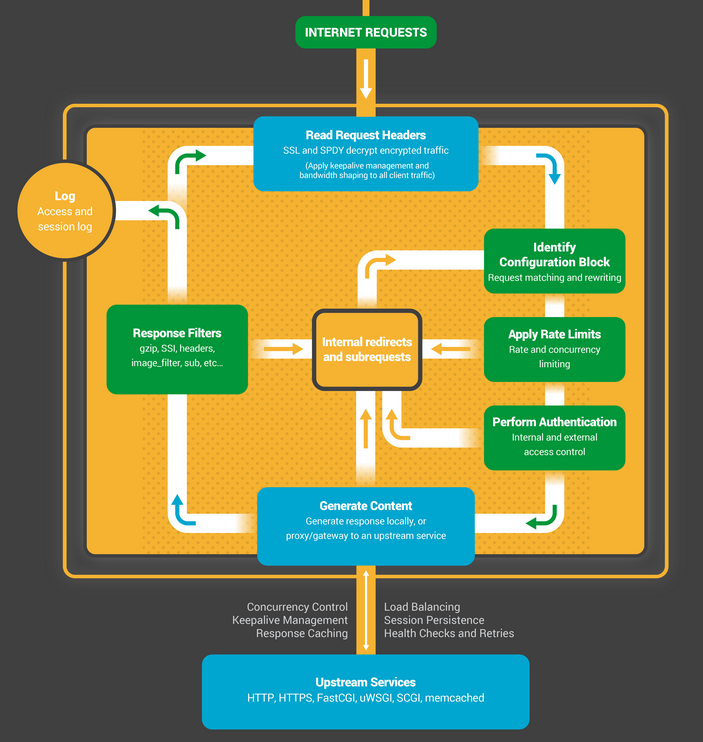
How Does NGINX work
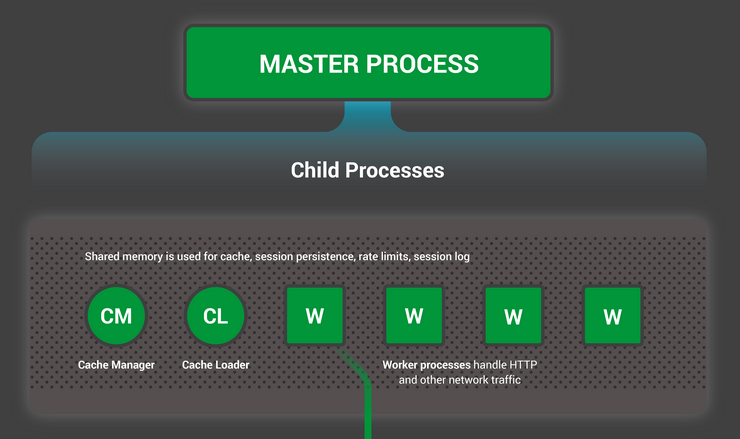
NGINX uses a predictable process model that is tuned to the available hardware resources:
- The master process performs the privileged operations such as reading configuration and binding to ports, and then creates a smalle number of child processes –
- The Cache loader processs runs at startup to load the disk-based cache into memory, and then exits. It is scheduled conservatively, so its resource demands are low.
- The cache manager process runs periodically and prunes entries from the disk caches to keep them within the configured sizes.
- The worker processes do all of the work! They handle network connections, read and write content to disk, and communicate with upstream servers.
Recommended: running one worker process per CPU core. –> configure by setting the auto param on the worker_processes directive.
Each worker process handles multiple connections in a nonblocking fashion, reducing the number of context switches.
Each worker process is single-threaded and runs independently, grabbing new connections and processing them. The processes can communicate using shared memory for shared cache data, session persistence data, and other shared resources.
Inside the NGINX worker process
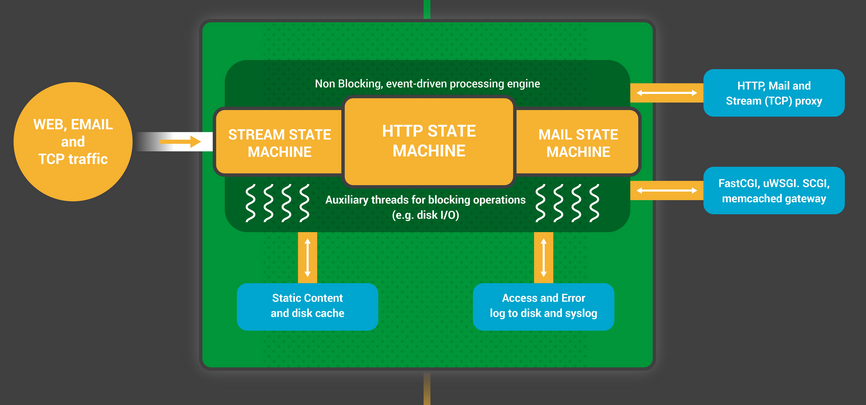
NGINX begin by waiting for events on the listen sockets. Events are initiated by new incoming connections. These connections are assigned to a state machine - commonly HTTP state machine.
State machine: essentially a set of instructions that tell NGINX how to process a request.
A blocking state machine
Most web servers and web apps use a process-per-connection or thread-per-connection model to process the HTTP transaction. During the time the process is run by the server, it spends most of its time “blocked” – waiting for the client to complete its next move.
- The web server process listens for new conntections on the listen sockets.
- When it get a HTTP transaction, it processes, blocking after each step to wait for the client’s responses.
- Once the game completes, the web server process might wait to see if the client wants to start a new transaction(keep alive connection). if the connection closed (client goes away or a timeout occurs), the web server process returns to listening for new games.
Problem: Imbalance in maps between the lightweight HTTP connection map t a separate thread or process, where HTTP connections represented by a file descriptor and a small amount of memory, and the thread or process often a heavyweight operating system.
How NGINX worker process: each worker handles hundreds of transactions simultaneously.
– Non-Blocking Event-Driven architecture.
- The worker waits for events on the listen and connection sockets.
- Event occur on the sockets and the worker handles them:
- An event on the listen socket means that a client has started a new chess game. The worker creates a new connection socket.
- An event on a connection socket means that the client has made a new move. The work responds promptly.
A worker never blocks on network traffic, waiting for clients to respond. When it has made its move, the worker immediately proceeds to other games where move are waiting to be processed, or welcomes new players in the door.
Proxy
A reverse proxy is a webserver that centralises internal services and provides unified interfaces to the public. Requests from clients are forwarded to a server that can fulfill it before the reverse proxy returns the server’s response to the client.
Additional benefit:
- Increased security - Hide information about backend servers, blacklist IPs, limit number of connections per client.
- Increased scalability and flexibility - Clients only see the reverse proxy’s IPs, allowing you to scale servers ot change their configuration.
- SSL termination:Decrypt incoming requests and encrypt server responses so backend servers do not have to perform these potentially expensive operations.
- Compression – Compress server responses
- Caching - Return the response for cached requests
- Static content - Serve static content directly
Loader balancer vs reverse proxy
- deploying a load balancer is useful when you have multiple servers. Often, loader balancer route traffic to a set of servers serving the same function.
- Reverse proxies can be useful even with just one web server or application server, opening up the benefits described.
- NGINX and HAProxy can support both layer 7 reverse proxy and load balancing.
Disadvantages: Reverse proxy
- increase complexity
- single reverse proxy - single point of failure, multiple reverse proxies - complexity.
Application Layer
Single Responsibility principle advocates for small and autonomous services that work together.
Microservices
Definition: a suite of independently deployable, small modular services. Each services runs a unique process and communicates through a well-defined, lightweight mechanism to serve a business goal.
Service Discovery
Systems like Consul, Etcd, and Zookeeper that help services find each other by keeping track of registered names, addresses, and ports. Both Consul and Etcd have a built-in key value store that can be useful for storing config values and other shared data.
Disadvantages
- Adding a application layer with loosely coupled services requires a different approach from an architectural, operations, and process viewpoint.
- Microservices can add complexity in terms of deployments and operations.
Database
Relational Database management system (RDBMS)
A collection of data items organized in tables
ACID is the properties of relational database transactions
- Atomicity - Each transaction is all or nothing.
- Consistency - Any transaction will bring the database from one valid state to another.
- Isolation - Executing transactions concurrently has the same results as if the transactions were executed serially.
- Durability - Once a transaction has been committed, it will remain so.
Scale Techniques:
- Master-slave replication
- Master-Master replication
- federation
- sharding
- denormalization
- SQL tuning
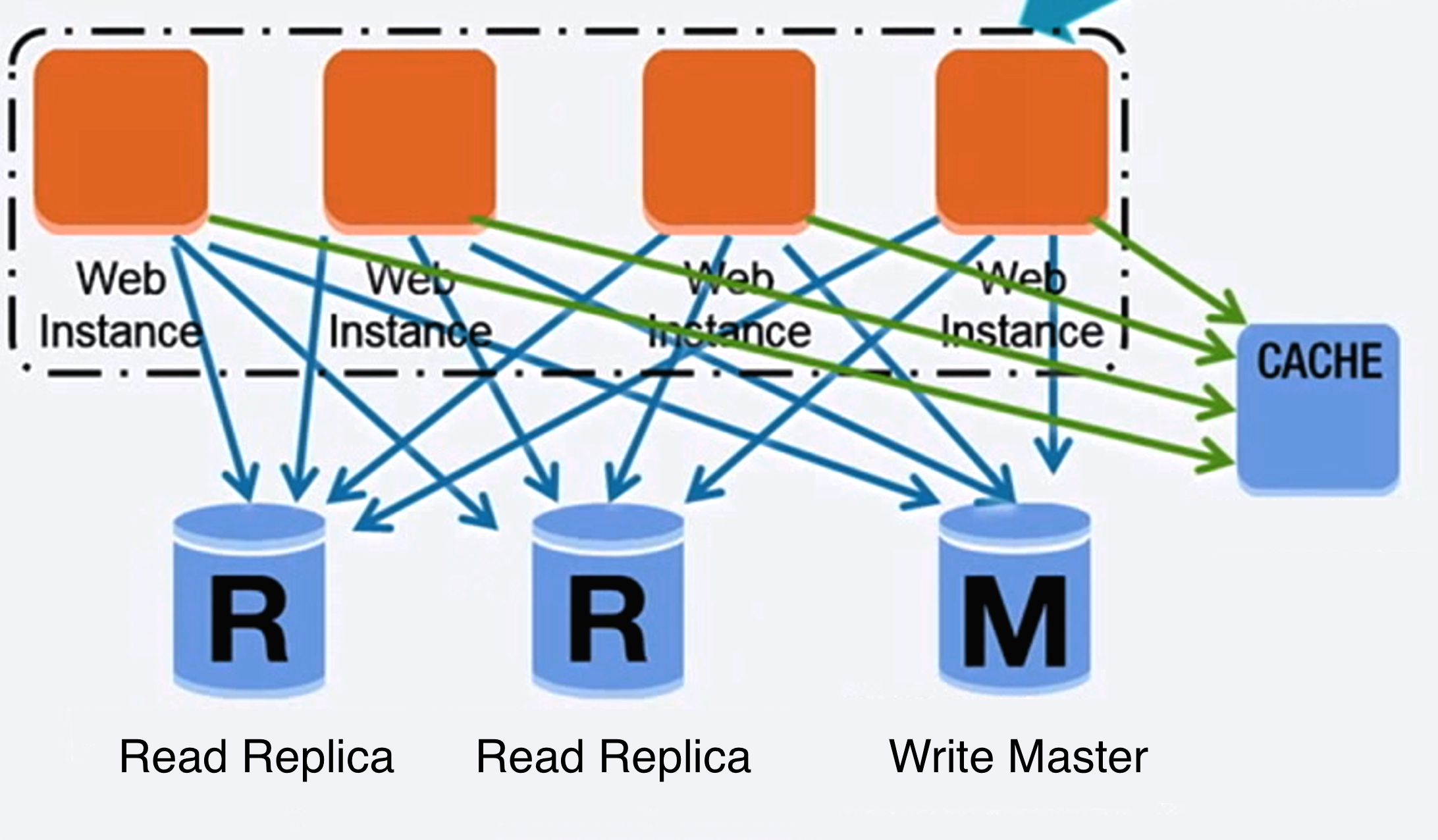
Master-Slave replication
Master serves reads and writes, replicating writes to other slaves, slaves only serve reads.
Slave can replicate read in tree fashion.
If Master go offline, system can still work in read only fashion.
Disadvantage
- Additional logic is needed to promote a slave to master
- Disadvantages for replication
Mater-Master replication
Both master serve reads and writes, and coordinate with each on writes.
If either master goes down, the system can continue to operate with both reads and writes.
Disadvantages
- Load balancer needed or changes needed to you application logic to determine where to write.
- Most master-master systems are either loosely consistent (violating ACID) or have increased write latency due to synchronization.
- Conflict resolution comes more into play as more write nodes are added and as latency increases.
- Disadvantages for replication.
Disadvantages for replication.
- Potential data loss if the master fails before any newly written data can be replicated to other nodes.
- Writes are replayed to the read replicas. If there are a lot of writes, the read replicas can stuck in replaying writes and cannot do many reads.
- Some system supports writing to master by spawning multiple threads to writes in parallel, but read replicas only support writing sequentially with single thread.
- Replication adds more hardware and additional complexity.
Federation
Federation (functional partitioning) splits up dataset by function.
Smaller dataset results in more data can fit in memory, results in more cache hit due to improved cache locality.
With no single central master serializing writes you can write in parallel, increasing throughput.
Disadvantages
- Federation is not effective if your schema requires huge functions or tables.
- You need to update your application logic to determine which database to read and write.
- Joining data from two databases is more complex with a server link.
- Federation adds more hardware and additional complexity.




Sharding
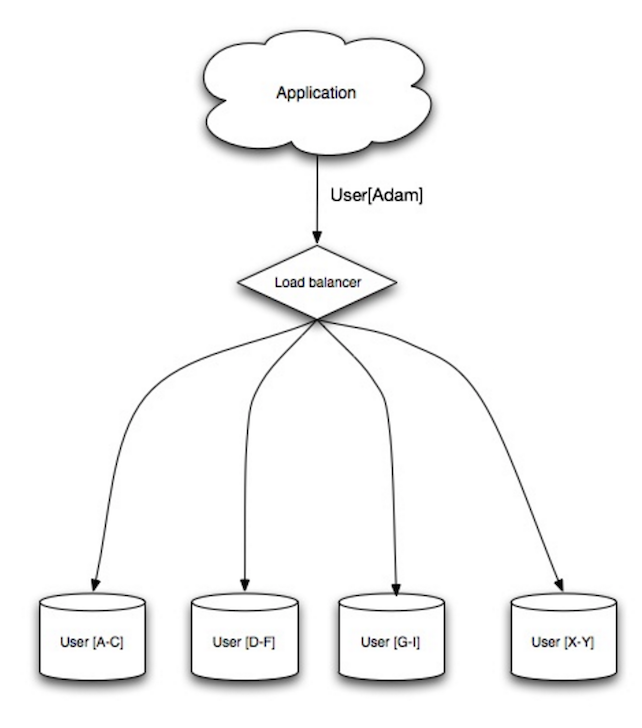
Sharding distributes data across different databases such that each database can only manage a subset of the data.
Taking a users database as an examples, as the number of users increases, more shards are added to the cluster.
Similar to advantages of federation, sharding results in less read and writes traffic, less replication, and more cache limits. index size is also reduced, which generally improves performance with faster queries.
No single central master serializing writes, allowing you to write in parallel with increased throughput.
Disadvantages
- you need to update your application logic to work with shards, which could result in complex SQL queries.
- Data distribution can become lopsided in a shard, for examples, a set of power users on a shard could result in increased load to that shard compared to others.
- Rebalancing adds additional complexity. A sharding function based on consistent hashing can reduce the amount of transferred data.
- Joining data from multiple shards is more complex.
- Sharding adds more hardware and additional complexity.
Denormalization 非规范化
Denormalization 通过牺牲一部分的写性能来获得更好的读性能. 通过在多个表中冗余数据副本来减少昂贵的join操作.
Some RDBMS like PostgreSQL and Oracle support materialized views 物化视图, can handle the work of storing information and keeping redundant copies consistent.
Once we use federation or sharding for distributed data, joins across data centers increases complexity. Denormalization can avoid the complex joins.
Disadvantages: Denormalization
- Data is duplicated
- Constraints can help redundant copies of information stay in sync, which increase complexity of the database design
- A denormalized database under heavy write load might perform worse than its normalized counterpart.
SQL tuning
It’s important to benchmark and profile to simulate and uncover bottlenecks
- Benchmark - simluate high-load siutations with tools such as ab.
- ab is a benchmarking tool for the Apache HTTP server. It is designed to give you an impression of how your current Apache installation performs. This especially shows you how many requests per second your Apache installation is capable of serving.
- Profile - Enable tools such as the slow query log to help track performance issues.
This might point to the following optimizations.
Tighten up the schema
- MYSQL dumps to disk in contiguous blocks for fast access.
- Use CHAR instead of VARCHAR for fix-length fields.
- CHAR allow for fast random access whereas with VARCHAR, you must find the end of the string before moving onto the next one.
- USE TEXT for large blocks such as long posts, TEXT also allows for boolean searches. Use TEXT results in storing a pointer on disk that is used to locate the text block.
Cache

Caching improves page load times and can reduce the load on your servers and databases.
Putting a cache in front of a database can help absorb uneven loads and spikes in traffic
-
Client caching
-
CDN caching
-
web server caching
Reverse proxies and caches such as varnish can serve static and dynamic content directly.
-
Database caching
Your database usually includes some level of caching a default configuration
-
Application caching
- In memory caches such as memcached and redis are key-value stores between application and your data storage.
- Cache invalidation algorithm such as LRU.
There are multiple levels for the caching, divided into two categories: database queries and objects
-
database queries
- row level
- query level
-
objects
- Fully-formed serializable objects
- Fully-rendered HTML
Generally you should try to avoid file-based caching, as it makes cloning and auto-scaling more difficult.
Caching at the database query level
hash the query as key and store the result to the cache.
Suffers from expiration issues.
- Hard to delete a cached result with complex queries
- If one piece of data changes such as a table cell, you need to delete all cached queries that might include the changed cell.
Caching at the object level
Have your application assemble the dataset from the database into a class instance or a data structure
- remove the object from cache if its underlying data has changed.
- Allow for asynchronous processing: workers assemble objects by consuming the latest cached object
Suggestions of what to cache:
- User sessions
- Fully rendered web pages
- Activity streams
- User graph data
When to update the cache