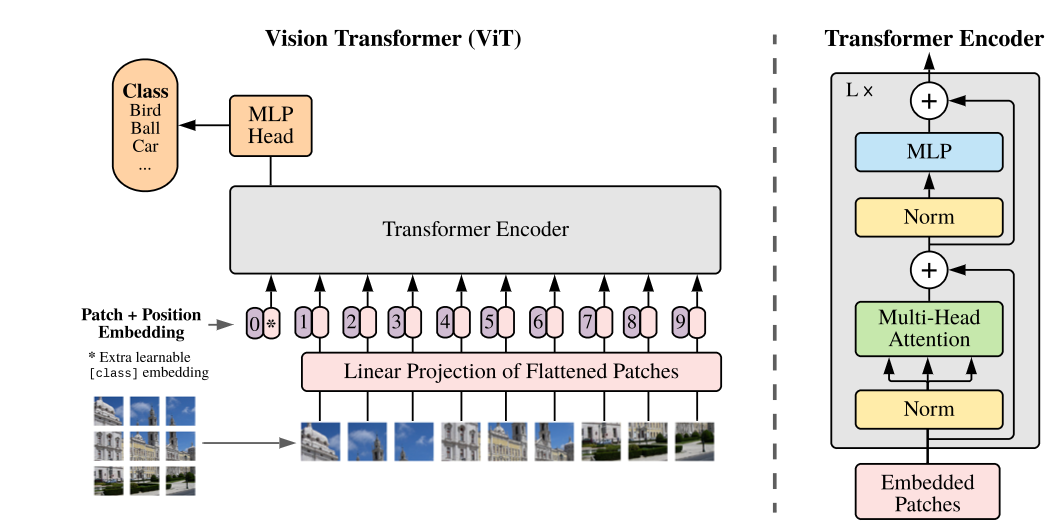
Vision Transformer (ViT)
Reshape the image $ x \in R^{H * W * C}$ into flattened 2D patches $x_{p} \in R^{N * (P^2 C)}$
$(H, W)$ the resolution of original image, $C$ channels, $(P,P)$ resolution for each image patch.
$N=HW / P^2$ the resulting number of patches.
Position Embeddings are added to the patch embeddings to retain positional information.
Inductive bias
ViT has much less image-specific inductive bias than CNNs.
Only MLP layers are local and translationally equivariant, while the self-attention layers are global.
Hybrid Architecture
The input sequence can be formed from feature maps of a CNN.
The patch embedding project is applied to patches from CNN feature map.
Fine-Tuning and Higher Resolution
The paper found that it performs better to fine-tune at higher resolution than pre-training.
The ViT can handle arbitrary sequence lengths but the pre-trained position embeddings may no longer be meaningful.
Point Cloud Transformer PCT
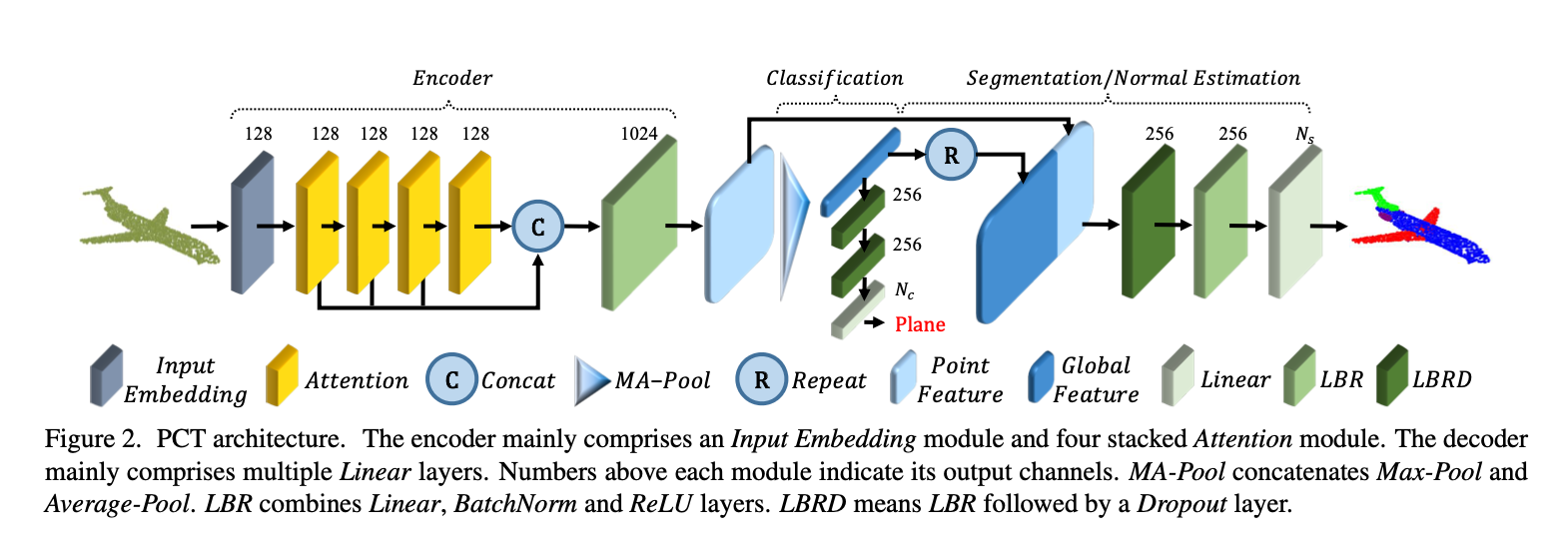
Encoder
- Embedding the input coordinates into a new feature space.
- Feed embedded features into 4 stacked attention module.
- To learn semantically rich and discriminative representation for each point
- A Linear layer to generate the output feature.
Compared to Ordinary Transformer:
- Share the same philosophy of design
- Positional embedding discarded, because coordinates already contains this info.
Formally:
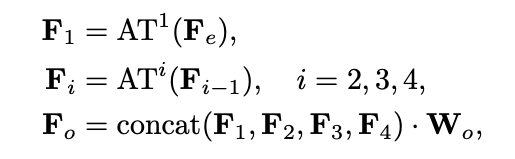
$F_e$ feature embedding for the point clouds.
$AT^i$ $i$_th attention layer.
$W_o$ weight for the linear layer.
Classification
- Feed global Feature $F_o$ to the classification decoder, consisting two cascaded feed-forward neural networks LBRs (Linear, BatchNorm, and ReLU layers), with dropout rate 0.5.
- A linear layer to predict the final classification scores $C \in R^{N_c}$ , determined as maximal score.
Segmentation
- Concatenate global feature $F_g$ with point-wise features in $F_o$.
- Encode the one-hot object category vector as 64-dim feature and concatenate it with the global feature.
- dropout only performed on the first LBR.
Normal Estimation
- Same architecture as in segmentation by setting $N=3$, without object category encoding.
- Regard the output point-wise score as the predict normal.
Naive PCT
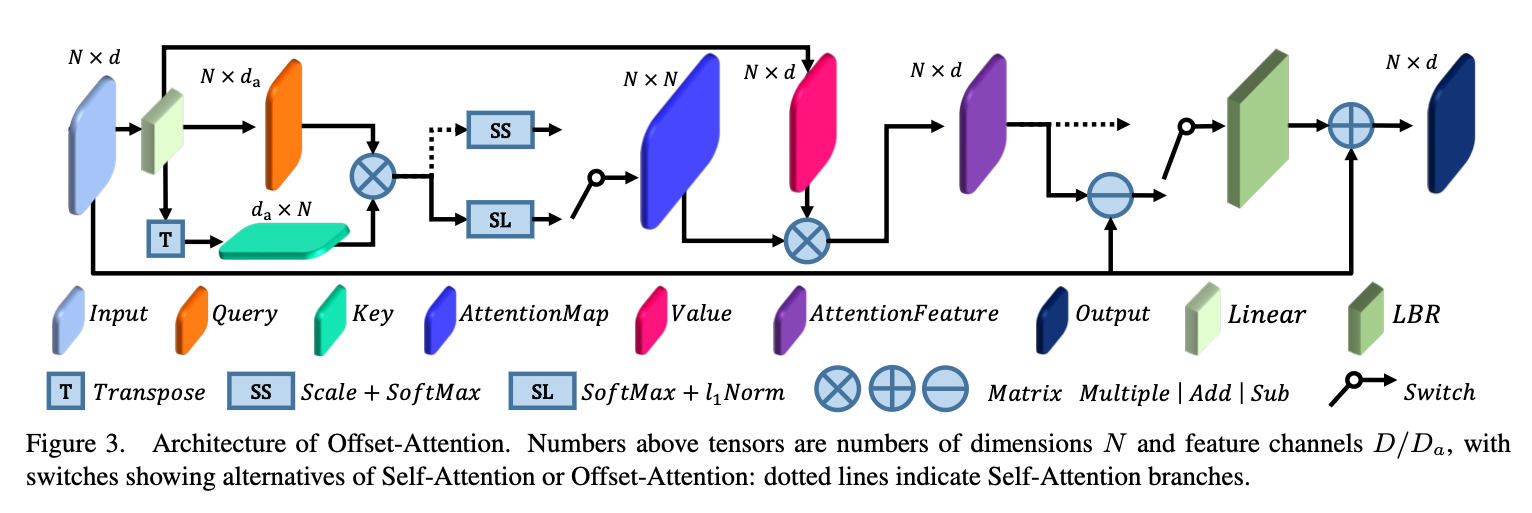
Offset Attention
Replace the Self-Attention module with Offset-Attention Module.
- The OA layer calculates the offset (difference) between the self-attention features and the input features by element-wise subtraction.
Neighbour Embedding
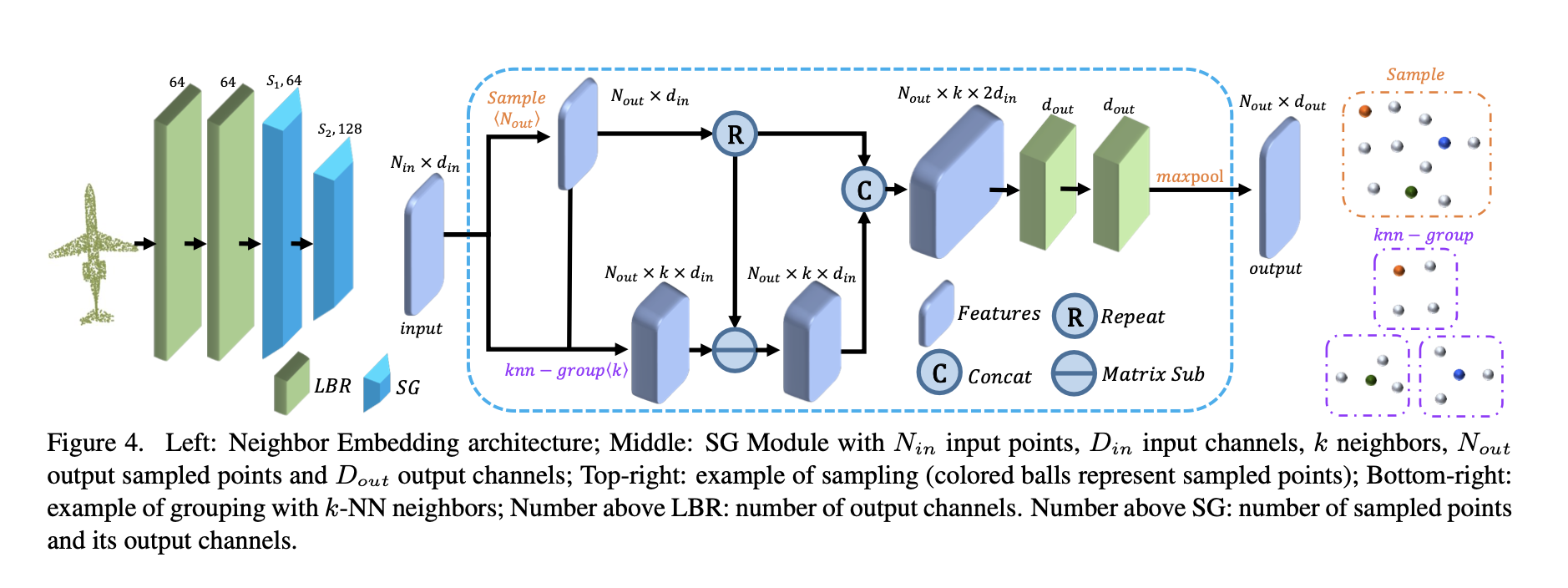
The Neighbour Embedding module contains two LBR layers and two SG (Sampling and grouping) layers.
The SG Layer
- Input point cloud $P$ with $N$ points and corresponding features $F$ , output a sampled point cloud $P_s$ with $N_s$ points and aggregated features $F_s$.
- Adopt Farthest point sampling (FPS) algorithm to downsample $P \rarr P_s$
- for each sampled point $p \in P_s$, $knn(p, P)$ is its $k$-nearest neighbours in $P$. The output feature is:
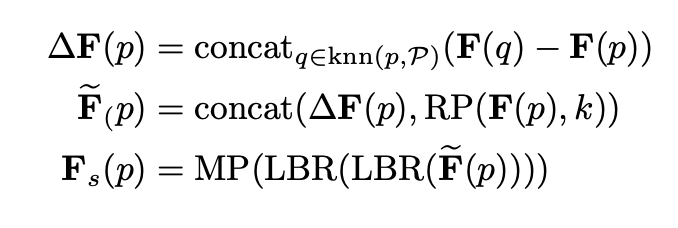
$F(p)$ the input feature of point $p$,
$F_s(p)$ is the output feature of sampled point $p$,
$MP$ is the max-pooling operator,
$RP(x, k)$ repeat vecotr $x$ in $k$ times to form a matrix. (idea from EdgeConv)